Source: The Third Affiliated Hospital
Written by: The Third Affiliated Hospital
Edited by: Wang Dongmei
Professor Gao Zhiliang’s team from the Department of Infectious Diseases of The Third Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University made a new breakthrough in the research of microenvironment of hepatocellular carcinoma, recently. The research results, entitled "The local immune landscape determines tumor PD-L1 heterogeneity and sensitivity to therapy", were published in
Journal of Clinical Investigation (IF = 12.282), an international well-known clinical research medical journal.
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most concerned problem in the field of liver disease. In 2016, The World Health Organization (WHO) warned that mortality in people with liver diseases might rise to 10 million by 2030; most of them would be caused by HCC.
Over the past few years, with the significant progress in the research of immune microenvironment of hepatocellular carcinoma, fundamental changes have taken place in the basic research and clinical treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. For example, monoclonal antibodies against immunosuppressive molecule PD-1/PD-L1 can restore the immune response to the microenvironment of hepatocellular carcinoma and have achieved remarkable clinical effects. However, even in sensitive (PD-L1+) patients with hepatocellular carcinoma, PD-1/PD-L1 antibodies are only effective in a small number of patients. Therefore, further investigation on the composition, function and shaping mechanism of PD-L1+ hepatocellular carcinoma microenvironment is expected to provide new target molecules as well as new intervention strategies for accurate immunotherapy of hepatocellular carcinoma.
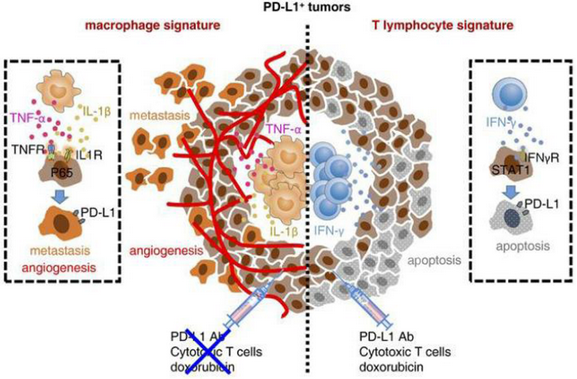
Illustration: The research found that there was high heterogeneity in the immune microenvironment of PD-L1+ hepatocellular carcinoma. A combination of immune checkpoint therapy and macrophage function regulation is expected to become a new strategy for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma.
The team of Professor Gao Zhiliang cooperated with the team of Professor Kuang Dong-Ming, a double-hired professor, with the support of The “13th Five-Year” National Science and Technology Major Project as well as the Key Project of National Natural Science Foundation of China. They found that there was high heterogeneity in the immune microenvironment of PD-L1+ hepatocellular carcinoma. The research confirmed that macrophages and inflammatory mediators released by T cells are involved in the formation of PD-L1+ hepatocellular carcinoma, but at the same time, macrophages endowed PD-L1+ hepatocellular carcinoma with the characteristics of resistance to traditional chemotherapy, T cell killing and immune checkpoint therapy. A combination of immune checkpoint therapy and macrophage function regulation is expected to become a new strategy for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. In the meantime, the above conclusions of the main research have been verified in a variety of human tumors simultaneously.



