Source: Sun Yat-sen Memorial Hospital
Edited by: Tan Rongyu, Wang Dongmei
Carcinoma-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) are activated fibroblasts that are key components of the tumor microenvironment. CAFs play a crucial role in tumor progression and have been implicated as promising targets for cancer treatments. However, phenotypic and functional heterogeneity of CAFs hinders this potential. Despite the increasing recognition of the functional diversity of CAFs, definitive surface markers in CAFs for precision therapies are still very limited. Dissecting the therapeutic value of CAF subset markers is important to design more effective therapies that leverage knowledge of the deleterious and beneficial roles of CAFs. Previously, Erwei Song and Shicheng Su’s team identified a subset of CD10+GPR77+ CAFs that promote tumor formation and chemoresistance by providing a survival niche for CSCs. The induction of CD10+GPR77+ CAFs is triggered by complement signaling via GPR77. CD10+GPR77+ CAFs sustain tumor stemness by the secretion of interleukin (IL)-6 and IL-8. However, the role of CD10 in CAFs is unknown. Recently, Shicheng Su from Sun Yat-sen Memorial Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University, revealed a new mechanism of breast cancer stemness sustained by CD10 expressed on cancer-associated fibroblasts. This work entitled " A CD10-OGP Membrane Peptolytic Signaling Axis in Fibroblasts Regulates Lipid Metabolism of Cancer Stem Cells via SCD1 ” is published in
Advanced Science on Aug. 7th, 2021. Prof. Shicheng Su from Sun Yat-sen Memorial Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University, is the only corresponding author. Shubin Yu, a doctoral student, Yiwen Lu, an associate research fellow, and An Su, a postdoctoral student are co-first authors.
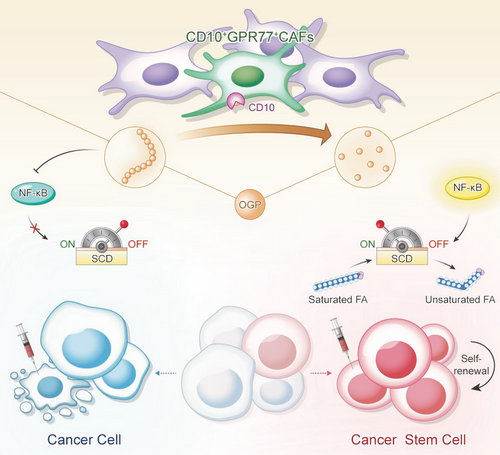
Here, the researchers demonstrate that CD10 expressed on a subset of CAFs supports tumor stemness and induces chemoresistance. CD10 is a transmembrane zinc-dependent metallopeptidase that hydrolyzes multiple bioactive peptides and plays a pivotal role in various diseases. To investigate whether CD10 in CAFs exerts its functions by mediating peptide degradation, they compared peptide profiles in interstitial fluid of breast cancer samples with high or low CD10+ CAF infiltration, and identified a peptide called osteogenic growth peptide (OGP), which is the main substrate of CD10 in tumors. In further investigation, they found that CD10 supports tumor stemness and induces chemoresistance mainly by degenerating OGP. Mechanistically, OGP restrains the expression of rate-limiting desaturase SCD1 and inhibits lipid desaturation, which is required for cancer stem cells (CSCs). CD10 hydrolyzes OGP and reverse its effect.
Collectively, Prof. Shicheng Su’s team reveal a cell surface peptolytic signaling axis present in a tumor-promoting CAF subset. The findings also raise the possibility that CAFs shape tumor cell fate by modulating their lipid metabolism. Besides, the findings reveal a functional marker of CAFs as a targetable metabolic vulnerability of CSCs, which can be exploited to improve existing therapies.
Link to the article:
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/advs.202101848



