Source: Zhongshan Ophthalmic Center
Edited by: Zheng Longfei, Wang Dongmei
Limbal stem/progenitor cells (LSCs) segregated in the basal layer of limbus undergo self-renewal and differentiation throughout life to maintain corneal epithelial homeostasis and regeneration. Genome topology provides a proper structural basis for TF- and epigenome-mediated transcriptional regulation in eukaryotes. In the previous study, Prof. Hong Ouyang’s mapped the epigenetic landscape of LSCs and identified an RUNX1/PAX6/SMAD3 complex-mediated chromatin regulatory network required for corneal epithelial identity and homeostasis. However, how genome topology couples with epigenetic states to govern the function and identity of the corneal epithelium are poorly understood.
Recently, Prof. Hong Ouyang’s team from the Zhongshan Ophthalmic Center of Sun Yat-sen University published a research article entitled “Comprehensive 3D epigenomic maps define limbal stem/progenitor cell function and identity” in
Nature communications. This work generates a high-resolution Hi-C interaction map of human LSCs. By integrating Hi-C, epigenome, TF binding profiles and transcriptome data, the authors characterize the comprehensive 3D epigenomic landscapes of LSCs.
In this study, the researchers characterize the multi-hierarchical genome organization of human LSCs, including chromosomal compartments, TADs and chromatin loops. The combination of chromatin organization, epigenome, TF occupancy and transcriptome creates comprehensive 3D epigenomic landscapes that contribute to gene activation and repression (Figure 1).
Figure 1 Schematic overview of the study
The inactive genome regions with exceptionally high densities of H3K27me3 or H3K9me2 are defined as super-silencers. These super-silencers maintain corneal epithelial identity and repress disease-associated genes through chromatin interactions and/or proximity (Figure 2).
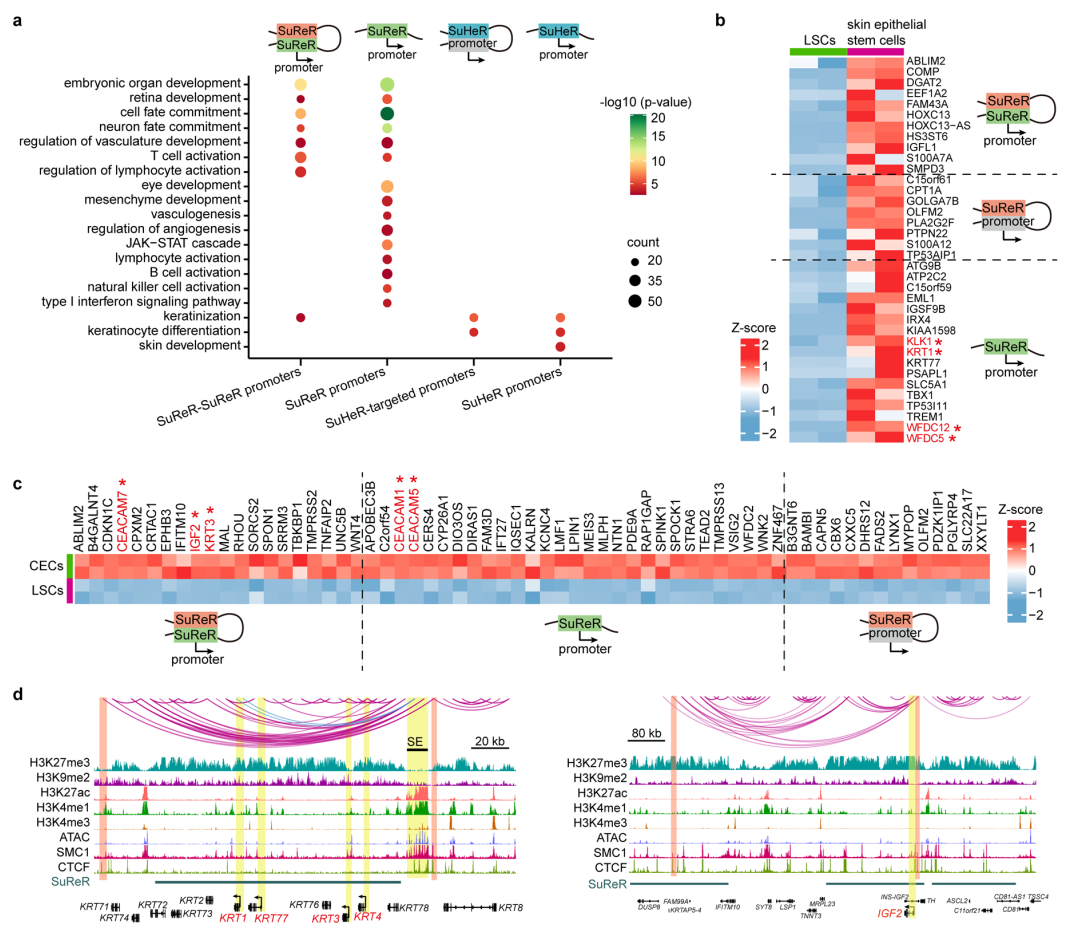
Figure 2 Super-silencers maintain LSC identity and repress disease genes via proximity and chromatin interactions
We construct super-enhancer (SE) interaction networks that regulate LSCfunction and identity. The identification of a cohort of intersected SE interaction hubs that contain multiple SE-SE and SE-promoter (SE-P) loops proposes a novel regulatory pattern of SEs. The active and inactive region-anchored interactions are associated with cohesion and largely occur within the cohesion-occupied CTCF-CTCF loop domains (Figure 3).
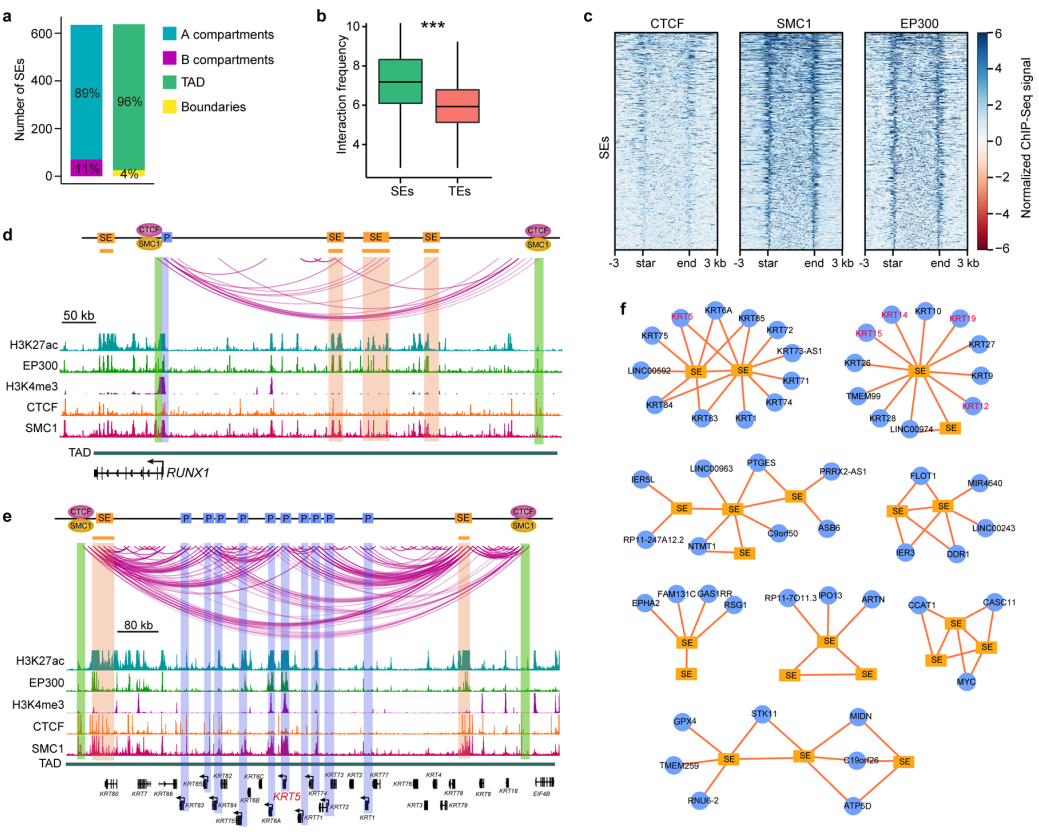
Figure 3 SE-anchored chromatin interaction networks
Collectively, this work provides detailed insights into the genome organization principle for epigenetic regulation of gene expression in stratified epithelia (Figure 4).
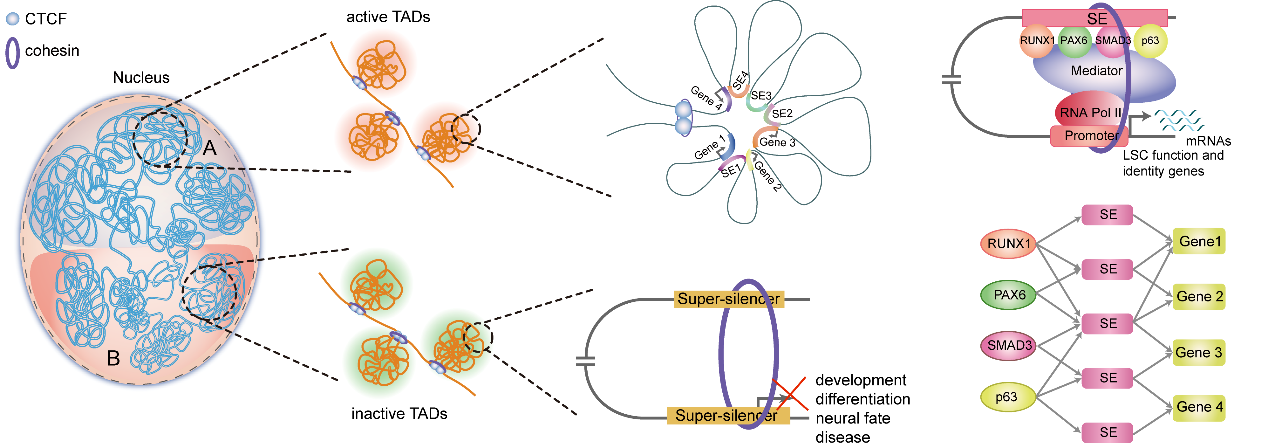
Figure 4 A model of 3D regulatory network organized into the multi-hierarchical genome architectures in LSCs
Link to the paper:
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-022-28966-6



