Depression is one of the most common mental disorders with the highest disability, affecting about 4.4% of the global population. Women are more likely to be affected by depression and develop more severe depressive symptoms than men, but the underlying mechanisms that contribute to sex difference of depression remain unclear.
The recently rediscovered meningeal lymphatic vessels are immune structures in the central nervous system that bridge brain and the peripheral immune system. A recent research article, published in Nature Communications by the team of Dr. Xiaojing Ye from Zhongshan School of Medicine of Sun Yat-sen University, together with Dr. Wei-Jye Lin from Sun Yat-sen Memorial Hospital and Dr. Yan Zhang from the Second Xiangya Hospital, finds that the meningeal lymphatic vessels play a critical role in the sex difference in stress susceptibility to depression.
The team revealed that sub-chronic variable stress induced depressive behaviors and accompanied by damages to the structure and drainage function of meningeal lymphatic vessels in female mice rather than male mice. Alteration of meningeal lymphatic vessels could change the susceptibility of female and male mice to stress-induced depressive and anxiety-like symptoms. The researchers further found that stress induced chemokine CCL6 to reduce meningeal lymphatic coverage, resulting in accumulation of triacylglycerols in the medial prefrontal cortex and ventral tegmental area, two brain regions that are critical for mood regulation.
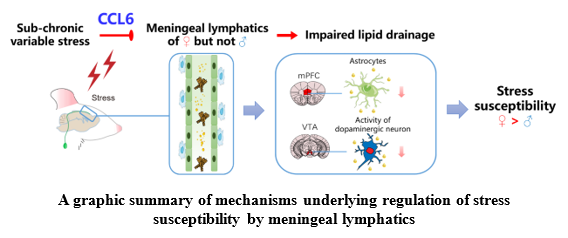
These findings reveal for the first time that injury of meningeal lymphatic vessels may be a key factor affecting the susceptibility of different sexes to cope with stress. The study also suggests the measurement of drainage function of meningeal lymphatics may serve as a novel biomarker for early diagnosis and prediction for the effectiveness of depression treatment in the clinics.
Graduate students Weiping Dai, Mengqian Yang and Pei Xia are co-first authors of the paper. Professors Xiaojing Ye, Wei-Jye Lin and Yan Zhang are the co-corresponding authors.
Link to the paper: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-022-32556-x



