Engineering functional inorganic–organic hybrid systems: advances in siRNA therapeutics
Source: School of Chemistry
Written by: School of Chemistry
Edited by: Wang Dongmei
Cancer treatment still faces a lot of obstacles such as tumor heterogeneity, drug resistance and systemic toxicities. Beyond the traditional treatment modalities, exploitation of RNA interference (RNAi) as an emerging approach has immense potential for the treatment of various gene-caused diseases including cancer. The last decade has witnessed enormous research and achievements focused on RNAi biotechnology. However, delivery of small interference RNA (siRNA) remains a key challenge in the development of clinical RNAi therapeutics. Indeed, functional nanomaterials play an important role in siRNA delivery, which could overcome a wide range of sequential physiological and biological obstacles. Nanomaterial-formulated siRNA systems have potential applications in protection of siRNA from degradation, improving the accumulation in the target tissues, enhancing the siRNA therapy and reducing the side effects.
In this review, we explore and summarize the role of functional inorganic–organic hybrid systems involved in the siRNA therapeutic advancements. Additionally, we gather the surface engineering strategies of hybrid systems to optimize for siRNA delivery. Major progress in the field of inorganic–organic hybrid platforms including metallic/non-metallic cores modified with organic shells or further fabrication as the vectors for siRNA delivery is discussed to give credit to the interdisciplinary cooperation between chemistry, pharmacy, biology and medicine.
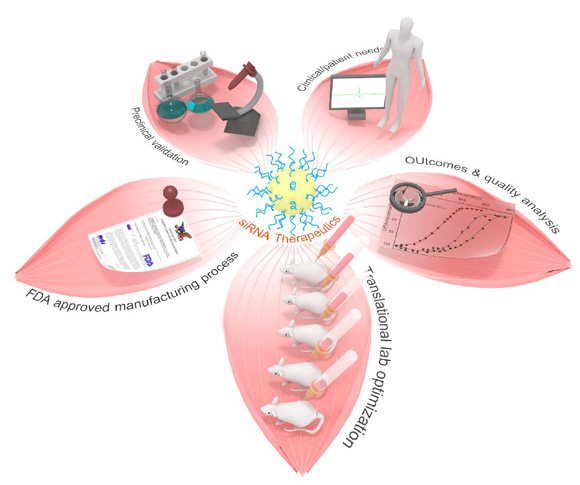
Inorganic–organic hybrid system formulated siRNA therapeutics for clinical needs.
This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21231007 and 21572282), the 973 program (No. 2014CB845604 and 2015CB856301), the Ministry of Education of China (No. IRT17R111), the Guangdong government (207999 and 2015A030306023) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities; the Wenzhou Medical University and Wenzhou Institute of Biomaterials & Engineering (WIBEZD2017001-03); the Houston Methodist Research Institute, and the National Institute of Health (1R01CA193880-01A1).
Link:
http://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2018/cs/c7cs00479f#!divAbstract
