A breakthrough in identifying and quantifying influential global spreaders in big-data social networks
Source: School of Data and Computer Science
Written by: School of Data and Computer Science
Edited by: Wang Dongmei
Recently,
PNAS, an international top comprehensive journal, published “Local structure can identify and quantify influential global spreaders in large scale social networks”, which is the latest scientific research about inforamtion spreading in online big-data social networks made by Associate Professor Yanqing Hu in School of Data and Computer Science at Sun Yat-sen University and his cooperators. The study reveals there are both global and local phases coexisting in spreading processes: for any stochastic spreading event, the information either spreads to a large amount of nodes, or is localized within a few spreading steps. These two phases are unambiguously separated by a local length scale, which leads to the following three surprising results: 1) In social networks, for a given spreading probability, the spreading power of the individual can be exactly defined as the product of the percolation component size and the probability that the individual is in the percolation component. 2) Any individual’s influence can be quantified from purely local network information within a characteristic influence radius. The influence radius is analogous to the correlation length in a percolation transition—there is a deep theoretical connection between this social phenomenon and the critical behaviour of a physical phase transition. 3) Based on the above physical findings, they design an optimization algorithm to select the set of most influential individuals. The algorithm does not require the global network information, and its computational time is extremely low and independent of the network size. Applying our algorithm to global OSNs like Facebook and Twitter is expected to reduce the computational time from century to seconds. Remarkably, it also provides nearly optimized solution. This result would have potential for practical applications in real big-data OSNs.
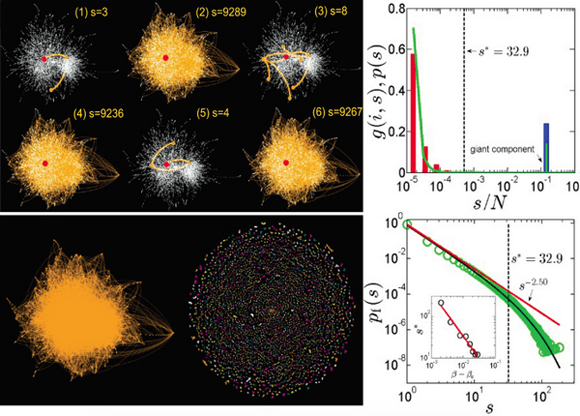
The local and global phases of information spreading process in online social networks
The earlier version of this paper was reviewed by high impact journal
Physics Reports (Vital nodes identification in complex networks) and comment our works as: “…by mapping the spreading dynamics (SIR family) onto bond percolation on complex networks, Hu et al. found a pivotal law central to SIR family spreading – the spreading occurs in one of the two states, local phase and global phase. This revealed a very fundamental and exciting result, that is, a node’s or a group of nodes’ global influence can be exactly measured by using purely local network information.”
Link to the paper:
http://www.pnas.org/content/early/2018/07/02/1710547115.short
