Prof. Wen-Jun Li's group at School of Life Sciences reveal the metabolism and evolution of the uncultivated archaeal phylum Aigarchaeota
Source: School of Life Sciences
Written by: School of Life Sciences
Edited by: Wang Dongmei
Prof. Wen-Jun Li's group at the School of Life Sciences, Sun Yat-sen University has published an article entitled "Genomic inference of the metabolism and evolution of the archaeal phylum Aigarchaeota" in the prestigious journal Nature Communications volume. The results of this study indicate that members of the phylum Aigarchaeota are either strict or facultative anaerobes, and most are chemolithotrophs that can perform sulfide oxidation. The Postdoctoral Research Associate Dr. Zheng-Shuang Hua and Research Assistant Yan-Ni Qu are the co-first authors of this paper, while Prof. Wen-Jun Li is the corresponding author of this study.
Members of the archaeal phylum Aigarchaeota are widely distributed in terrestrial and subsurface geothermal systems and marine hydrothermal environments. However, little is known about Aigarchaeota’s ecological role or evolutionary history. Six Aigarchaeota metagenomic bins were obtained from two circumneutral hot springs in Tengchong, the largest and most intensively studied geothermal field in China (Figure 1). Our analysis revealed a facultative or strictly anaerobic lifestyle of Aigarchaeota with an ability to oxidize sulfide to gain energy for growth (Figure 2). Evolutionary genomic analyses of Thaumarchaeota and Aigarchaeota suggested that both the phyla evolved from hot habitats and they shared a large proportion of gene families with their last common ancestor. Adaptation to a different habitat led to the functional differentiation of Aigarchaeota from Thaumarchaeota, with the latter invading a wide diversity of non-thermal environments (Figure 3). Genes acquired horizontally from Euryarchaeota and Firmicutes played a significant role in the functional diversification of Aigarchaeota in hot spring habitats. This study represented a significant advancement in our understanding of the genomic diversity and evolution of Aigarchaeota. This work also highlights the extraordinary diversity of microbial life still awaiting discovery in terrestrial geothermal systems.

Figure 1. The great boiling spring in the Rehai geothermal field in Tengchong, Yunnan Province, China
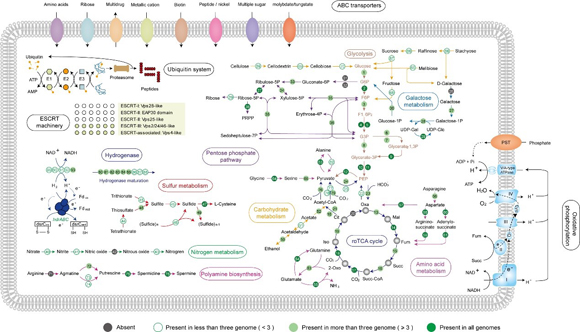
Figure 2. Overview of metabolic potentials in Aigarchaeota
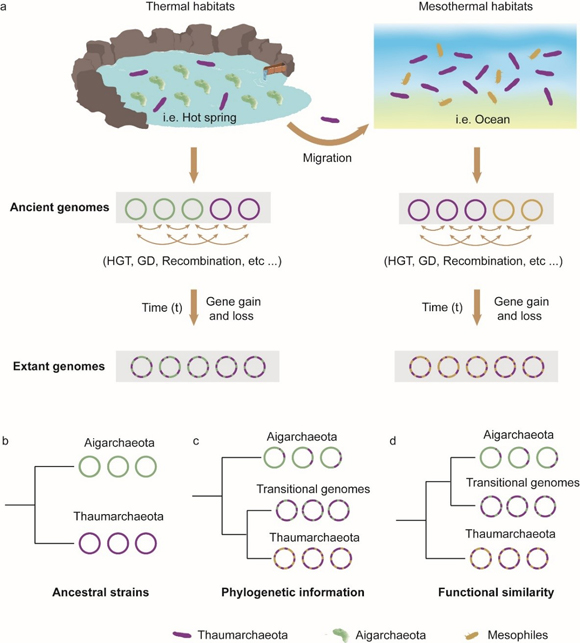
Figure 3. (a) The underlying model of the evolutionary history for Aigarchaeota and Thaumarchaeota; (b) The phylogeny of the ancestral strains of Aigarchaeota and Thaumarchaeota; (c) The tree shows the phylogeny of extant genomes of the two phyla; (d) The topology of the clustering based on the functional similarity for the two phyla
This work was supported by the Science and Technology Infrastructure work project of China Ministry of Science and Technology, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, and Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province, China.
Link to the article: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-018-05284-4
Link to the Prof. Wen-Jun Li's Lab: http://liactlab.sysu.edu.cn/index-en.html
