Professor Yue-Qin Chen and Associate Professor Yu-Chan Zhang’s Group at School of Life Sciences unveiled the function of reproductive phasiRNAs during meiosis in rice
Source: School of Life Sciences
Edited by: Tan Rongyu, Wang Dongmei
Plant spermatogenesis is a complex process that directly affects crop breeding. Meiosis is important for early male gametogenesis. A rapid change in gene abundance occurs at early meiosis prophase, when gene regulation is selective. However, how these genes are regulated remains unknown. Notably, a group of 21-nucleotide (nt) phased secondary siRNAs (phasiRNAs) exhibit a burst of expression in grass inflorescences from the premeiosis stage and to decrease in expression at the end of meiosis, when extensive gene expression changes occur, but their function is unclear.
Recently, a study accomplished by Professor Yue-Qin Chen and Associate Professor Yu-Chan Zhang from School of Life Sciences at Sun Yat-sen University revealed that rice reproductive phasiRNAs are essential for the elimination of a specific set of RNAs during meiotic prophase I by combining multi-omics sequencing and functional analysis in a transgenic plant series. This study reported that AGO protein MEL1–phasiRNAs are essential for trans RNA cleavage and mRNA elimination during meiotic prophase I. These phasiRNAs cleave target mRNAs in a regulatory manner such that one phasiRNA can target more than one gene, and/or a single gene can be targeted by more than one phasiRNA to efficiently silence target genes (Figure 1). Investigation of phasiRNAs knockdown and PHAS-edited transgenic plants demonstrates that phasiRNAs and their nucleotide variations are required for meiosis progression and fertility. This study highlights the importance of reproductive phasiRNAs for the reprogramming of gene expression during meiotic progression and establishes a basis for future studies on the roles of phasiRNAs with a goal of crop improvement.
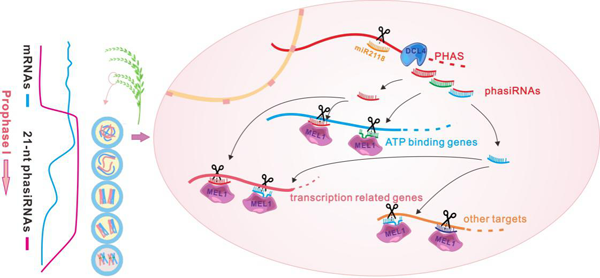
Figure 1. A working model for reproductive phasiRNAs which cleave and regulate target genes during meiotic prophase I in rice.
The study entitled “Reproductive phasiRNAs regulate reprogramming of gene expression and meiotic progression in rice” was published online in
Nature Communications on November 27, 2020. Professor Yue-Qin Chen and Associate Professor Yu-Chan Zhang were listed as the co-corresponding authors where Yu-Chan Zhang and Meng-Qi Lei (Ph.D. candidate) were listed as the co-first authors. This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China and grants from Guangdong Province.
This team focuses on the function of plant non-coding RNAs associated with crop agronomic traits. It is worth mentioning that they have also reported the function of another kind of small noncoding RNA miR528 in regulating pollen grain development in rice, which was published in
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (
PNAS) early this year.
Access to the papers:
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-020-19922-3
https://www.pnas.org/content/early/2019/12/20/1810968117
