Prof. Shixiao Yu’s group at School of Life Sciences made significant progress in the biodiversity maintaining mechanisms of forest communities
Source: School of Life Sciences
Written by: School of Life Sciences
Edited by: Tan Rongyu, Wang Dongmei
Biodiversity is the foundation of sustainable development for human society, and the guarantee of ecological civilization construction and national sustainable development. However, environmental pollution, climate change and habitat fragmentation caused by human activities have led to a significant loss of biodiversity worldwide. The study of species coexistence concerns the natural species diversity, which has been listed as one of the 25 most challenging global major topics.
Recently, Prof. Shixiao Yu’s team from School of Life Sciences published a research paper entitled “Soil fungal networks maintain local dominance of ectomycorrhizal trees” online in
Nature Communications, which revealed the critical role of underground fungal networks (the “wood-wide web”) in facilitating seedling growth and fitness, and consequently promoted the species diversity and community structure in subtropical forests. Dr. Minxia Liang from the Yu lab is the first author, and Prof. Xubing Liu is the corresponding author.
This research was conducted at the Heishiding Nature Reserve, which is also one of the field scientific observation and research stations of the Ministry of Education. The study reports findings from experiments undertaken at large temporal and spatial scales, and provides a mechanism explaining co-existence of trees in hyper-diverse forests of significant ecological and economic importance, and conservation concern. The authors integrated a long-term field investigation on seedling dynamics, which was undertaken at unprecedented temporal and spatial scales, including censusing 17,824 individual seedlings over ten years within 1200 1-m2 quadrats in the field. These surveys showed that survival of arbuscular mycorrhizal seedlings over ten years was negatively related to the density of surrounding conspecific plants, whereas the opposite was seen for ectomycorrhizal seedlings.
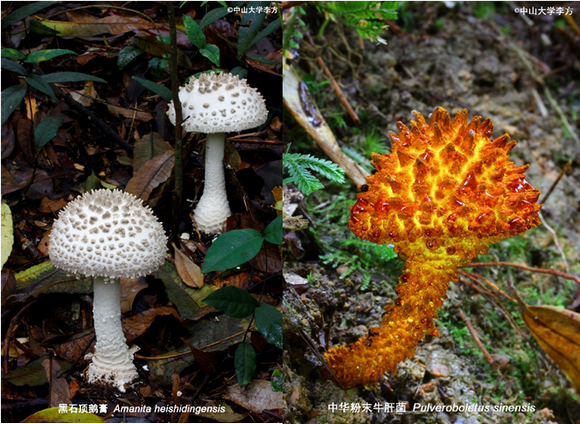

Figure 1 Two endemic ectomycorrhizal species at Heishiding Nature Reserve
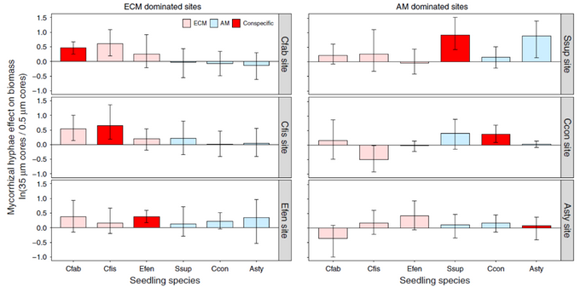
Figure 2 Effect of mycorrhizal hyphal connections on seedling survival and growth for ECM and AM tree species
The study found that the survival and fitness of ectomycorrhizal plants, which become canopy-dominants in these forests, increased markedly when plants could connect to fungal networks associated with neighbouring adult trees. Surprisingly, fungal networks did not affect arbuscular mycorrhizal seedling survival, and these species are usually restricted to the understory. This striking difference between species possessing different types of mycorrhizal association, which is demonstrated here for the first time, provides a mechanistic explanation for the local dominance of ectomycorrhizal trees in hyper-diverse subtropical and tropical forests. Moreover, the lack of any apparent effect of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal networks on seedling growth challenges the emerging popular, altruistic view that adult trees, regardless of mycorrhizal type, use fungal networks to support neighbouring seedlings.
The complementary molecular, manipulative and census-based experiments provide confidence that the patterns observed in the data are broadly applicable. These findings therefore make a step-change in our understanding of the processes regulating species coexistence and dominance in subtropical forests, and emphasize the critical role of mutualistic fungal networks and pathogenic fungi in these processes. The data show that fungal networks and interactions with pathogens are a critical factor explaining global patterns of ectomycorrhizal and arbuscular mycorrhizal trees in forests.
This research was funded by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Project No. 2017YFA0605100) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC 31770466 to X.L. and 31870403 to M.L.), and partly supported by awards from the UK Natural Environment Research Council (NERC NE/M004848/1 and NE/R004986/1).
Link to the paper:
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-020-16507-y
