The Planetary Environmental and Astrobiological Research Laboratory (PEARL) team from School of Atmospheric Sciences discovered the dust tides phenomenon on Mars
Source: School of Atmospheric Sciences
Written by: Zhaopeng Wu
Edited by: Xu Jia, Wang Dongmei
Mars, one of the most important terrestrial planets, shares many similarities with Earth. The comparative study of the climate between the two planets is of great significance for us to understand the evolution of the Earth's atmosphere. The climate change on Mars is directly related to the existence of water, which makes the study of the Martian atmosphere a key part in the exploration of extraterrestrial life and habitability.
As a desert planet, Mars is full of dust particles both on the ground and in the atmosphere. The dust cycle is as an extremely important component of the climate system to Mars, as the water cycle to Earth. Recent satellite observations have found that important volatiles in the Martian atmosphere, such as H2O and HDO, can be rapidly lifted from the troposphere to a hundred of kilometers just in a few days by deep convection during major dust storms. These new findings suggest that the short-period dynamics in the Martian atmosphere may be particularly important. However, previous studies were mostly focused on climatology of Martian airborne dust, while little is known about short-period processes dominated by extreme weather, such as the frequently-occurred dust storms on Mars.
Recently, Dr. Zhaopeng Wu and Dr. Jing Li, postdoctoral fellows of the Planetary Environmental and Astrobiological Research Laboratory (PEARL, led by Prof. Jun Cui), School of Atmospheric Sciences, Sun Yat-sen University, in collaboration with Prof. Tao Li from University of Science and Technology of China and Prof. Xi Zhang from University of California, Santa Cruz, USA, published an academic paper entitled "Dust Tides and Rapid Meridional Motions in the Martian Atmosphere During Major Dust Storms" in
Nature Communications, which reveals the commonly existed dust tide phenomenon during major dust storms on Mars and proposes a new hypothesis for the rapid transport of water vapor during global dust storms.
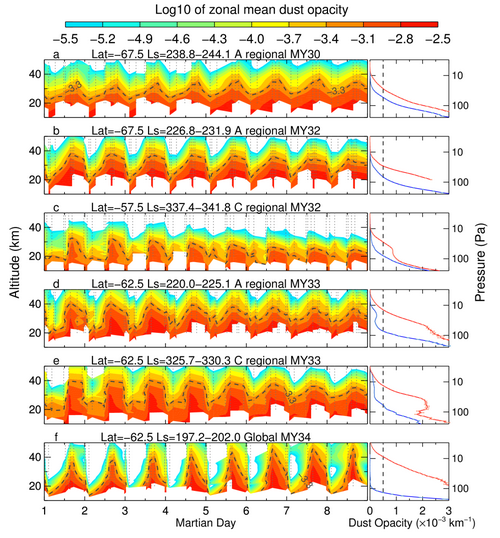
Figure 1. Diurnal variations of dust during major dust storms on Mars
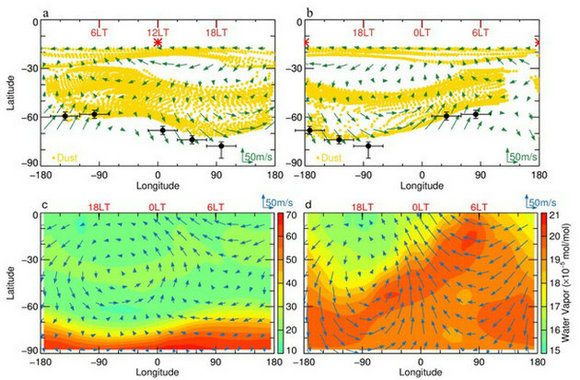
Figure 2. The dust diurnal motion (yellow dots) driven by the tidal wind (arrows) in the Southern Hemisphere of Mars (a, b), the red star represents the position of the sun, LT represents the local time; the water vapor diurnal motion (color) driven by the wind field (arrows) in the Southern Hemisphere of Mars during non-dust-storm condition (c) and the global dust storm in Mars Year 28 (d).
Using observations from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter, Wu et al. focused on major dust storms occurred in the last seven Mars years at a horizontal scale of thousands of kilometers or even global-encircling. They found strong diurnal change of dust in the upper troposphere at high latitudes of the Southern Hemisphere (Figure 1). Further observations indicated that this phenomenon is due to zonally distributed dust fronts sloshing back and forth in a wide latitudinal range within one Martian day. As an inert and globally distributed species in the Martian atmosphere, dust can be treated as an ideal tracer to track the wind field, which is difficult to directly measure by instruments. Therefore, the rapidly meridional motion of the dust front implies strong diurnal meridional winds. Using these dust observations, along with atmospheric tidal theoretical models, Wu et al. concluded that the dust tide phenomenon is driven by the westward-propagating migrating diurnal thermal tide—a global oscillation excited by solar heating in the atmosphere with a period of a solar day. This phenomenon indicates that the Martian atmosphere has rapid meridional motions during dust storms. Further investigation combined with the numerical simulation result from Mars Climate Database version 5.3 suggested that the nighttime tidal wind can transport water vapor from the polar reservoir to the mid-to-low latitudes during the global dust storm in Mars Year 28 (Figure 2). This water vapor can be lifted to the middle and upper atmosphere by daytime deep convection at mid-to-low-latitude, which contributes to water escape from Mars.
The new findings indicate a different mechanism for heat and material exchange between the high and middle latitudes on Mars from that on Earth. The meridional exchange on Earth is strongly dependent on the influence of Rossby waves. Although atmospheric thermal tides are also well-known atmospheric waves on Earth, they are mainly confined at tropics while have little effect at mid-to-high latitudes. However, the thin atmosphere of Mars can significantly enhance the role of thermal tides. This study has shown that the tidal wind plays an important part in the horizontal motion of the Martian atmosphere, which provides new insights into the mid-to-high-latitude exchange of planetary atmosphere.
Dr. Zhaopeng Wu, School of Atmospheric Sciences, Sun Yat-sen University, is the first author. Dr. Zhaopeng Wu and Professor Tao Li from University of Science and Technology of China are corresponding authors. This study was supported by the B-type Strategic Priority Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, the pre-research project on Civil Aerospace Technologies of China National Space Administration, the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the grant from Key Laboratory of Lunar and Deep Space Exploration, Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Link to the paper:
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-020-14510-x