
Source: The Sixth Affiliated Hospital
Edited by: Zheng Longfei, Wang Dongmei
The National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) is an academic organization composed of multiple cancer centers with a high reputation. NCCN publishes the updated NCCN guidelines for various malignant tumors every year based on the evidence from the latest publications. The NCCN guidelines have become the most widely used clinical guidelines in global clinical oncology practice and have been followed by clinicians worldwide.
Recently, an original research on the diagnosis and treatment of rectal cancer was completed by the group led by Drs Yanxin Luo and Huichuan Yu at the Sixth Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University. This article entitled “Current Surveillance After Treatment is Not Sufficient for Patients With Rectal Cancer With Negative Baseline CEA” has been published in the Journal of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (JNCCN, IF= 11.908), which is the official journal of the NCCN. Dr Huichuan Yu is the corresponding author, and Dr Dingcheng Shen is the first author.
Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) is a tumor-associated antigen first identified and isolated from colon cancer and embryonic tissues by Gold and Freedman in 1965. CEA is easy to be detected in human organs, tissues and various body fluids, and the detection has the advantages of non-invasiveness, accessibility and cost-effectiveness. The clinical practices have proved that CEA, as a broad-spectrum tumor biomarker, has critical clinical value in evaluating therapeutic effect and monitoring disease progression for multiple tumors such as digestive tract tumors, urinary tract tumors, lung cancer, ovarian cancer and breast cancer. The reference value of serum CEA is 0 to 5ug/L, which depends on the laboratory assays applied to determine CEA.
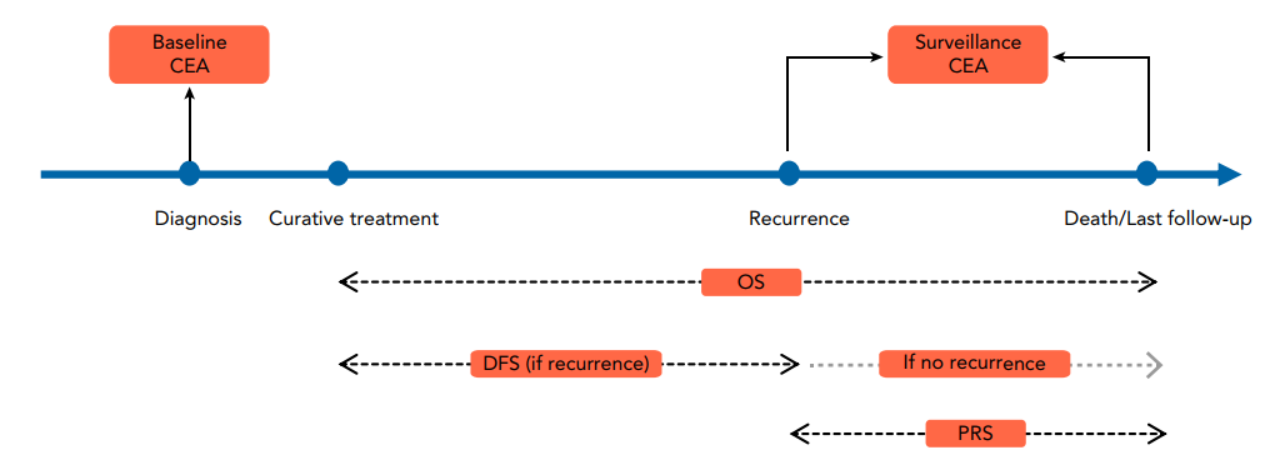
According to the NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines for Rectal Cancer, serum CEA is a crucial test in surveillance for rectal cancer after treatment, and serial CEA elevation is regarded as a strong marker for potential recurrence that requires more examination or intensive surveillance to confirm it (Figure 1).

However, during clinical practice, the team found that the performance of CEA in surveillance after treatment is not sufficient in the rectal cancer patients with normal baseline CEA. Therefore, the team conducted a longitudinal analysis based on the prospectively collected cohort of patients with rectal cancer to determine the diagnostic performance of CEA in surveillance for patients with different baseline CEA (Figure 2).
This study revealed that elevated CEA levels during surveillance after treatment presented with insufficient sensitivity for the detection of recurrence in patients with negative baseline CEA compared with those with elevated baseline CEA. Furthermore, the addition of CA19-9 to the CEA assay significantly improved the sensitivity in recurrence surveillance for patients with negative baseline CEA. Therefore, the current CEA-based surveillance protocols were insufficient for patients with negative baseline CEA, and the team led by Dr Huichuan Yu recommended that the baseline CEA level should be considered and stratified before CEA can be applied in the surveillance protocol of the NCCN Guidelines. They proposed an updated and more efficient surveillance protocol for patients with rectal cancer in the clinical setting (Figure 3).

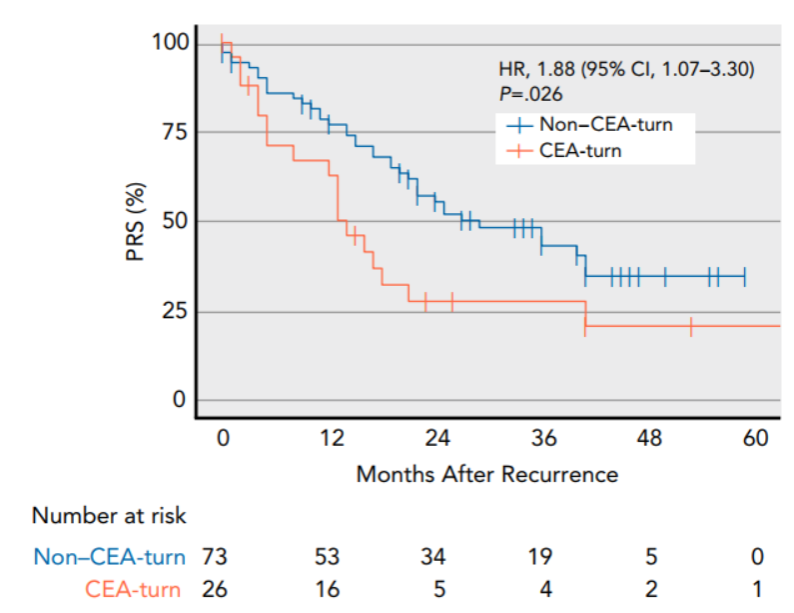
In addition, they identified a subgroup of CEA-turn tumors characterized by negative CEA at baseline and elevated CEA at recurrence. The patients with CEA-turn tumors were recognized with more aggressive diseases and worse survival outcomes after recurrence (Figure 4).
The Sixth Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University has one of the largest gastrointestinal cancer centers nationwide. Multiple national guidelines such as "Chinese Protocol of Diagnosis and Treatment for Colorectal Cancer" and "Chinese Guideline for the Screening, Early Detection and Early Treatment of Colorectal Cancer", multiple National Key Research and Development Projects, and a series of scientific and technological innovation achievements that have been industrialized were led and completed at The Sixth Affiliated Hospital. More than 110,000 case-times have been followed up in the institutional database of gastrointestinal tumors, and nearly 30,000 colorectal cancer patients (including radiotherapy and chemotherapy) were treated each year in the center with a five-year overall survival rate as high as 78%. The resource at The Sixth Affiliated Hospital provided support for the current study. The results of the present study may provide a valuable reference for developing and interpreting the next-generation surveillance protocols for colorectal cancer in clinical guidelines, which could help improve the treatment outcomes of patients.
Link to the paper: https://jnccn.org/view/journals/jnccn/aop/article-10.6004-jnccn.2021.7101/article-10.6004-jnccn.2021.7101.xml